An Advanced Surrogate Model Approach for Enhancing Fluid Dynamics Simulations
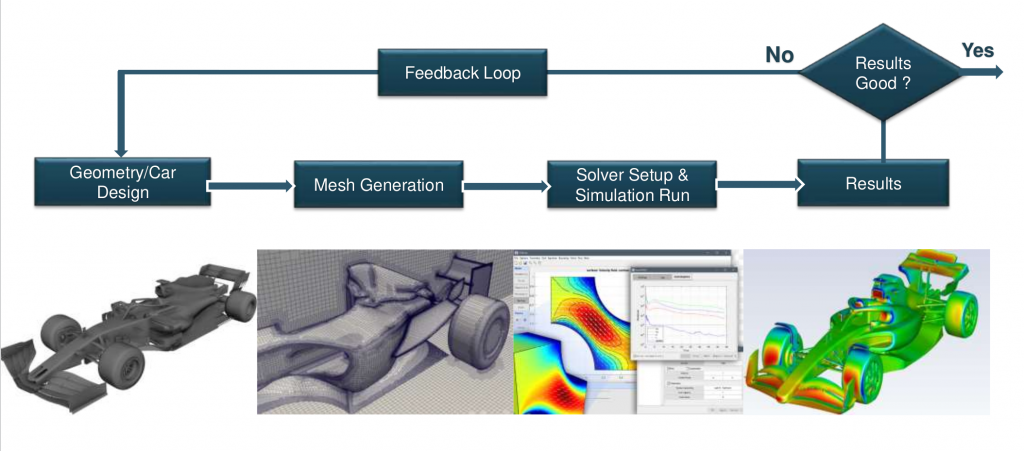
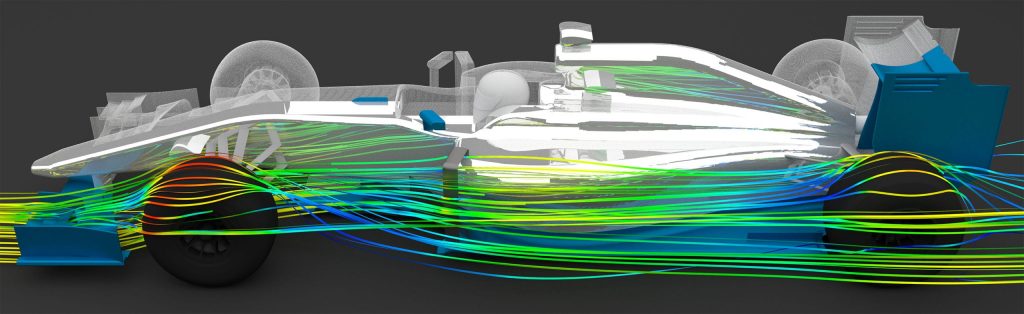
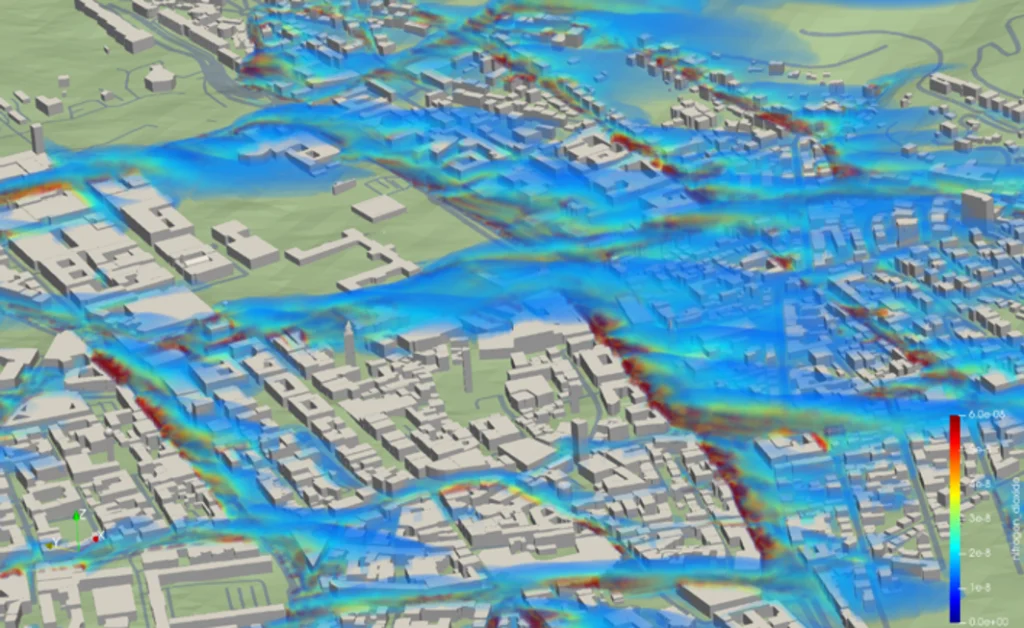
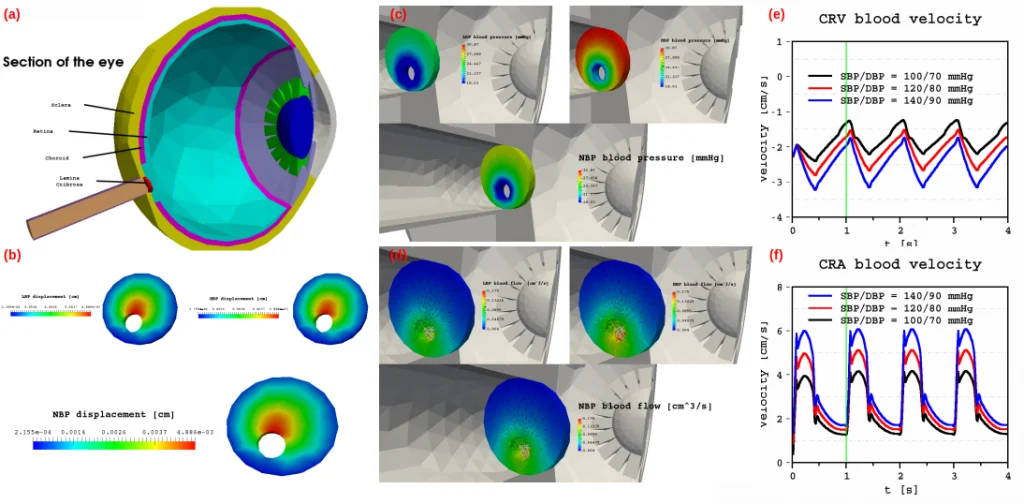
An advanced deep learning surrogate model trained on CFD data achieves high-fidelity fluid dynamics predictions at a fraction of the computational cost, accelerating simulation workflows.
An Advanced Surrogate Model Approach for Enhancing Fluid Dynamics Simulations Read More »